Obesity is a global public health problem that affects millions of people worldwide. In addition to the physical and aesthetic challenges it presents, obesity is also closely related to a number of comorbid diseases, which are additional medical conditions that can arise as a result of obesity. These diseases, which include type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, cardiovascular disease, sleep apnea and dyslipidemia, among others, can have a significant impact on the quality of life and life expectancy of affected individuals.
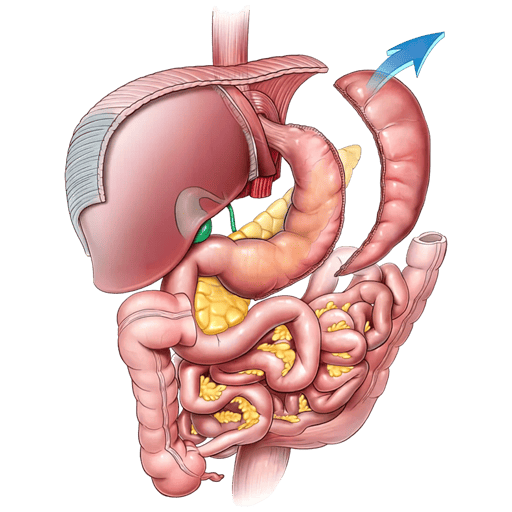
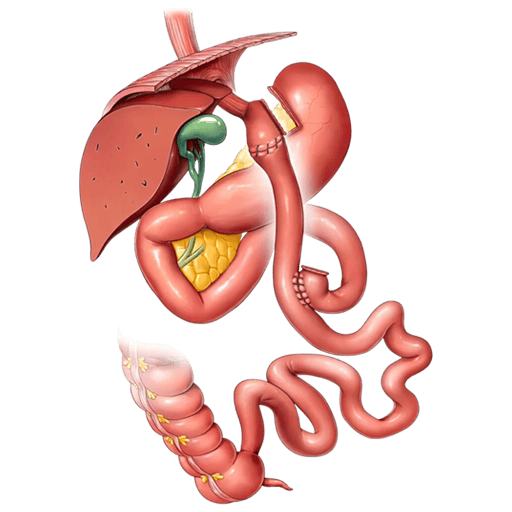
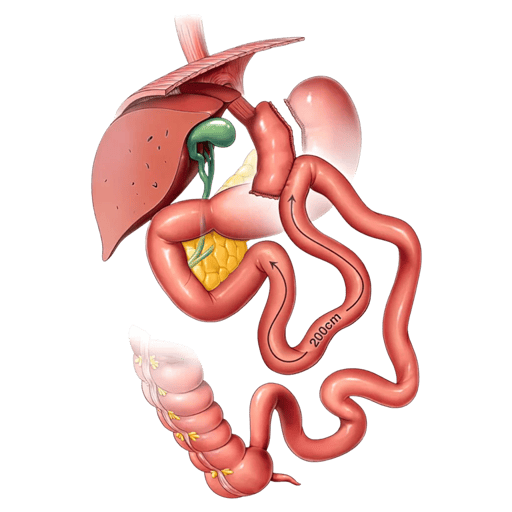
The bariatric surgery has emerged as an effective option for the treatment of severe obesity and its associated diseases. This surgical procedure, which includes techniques such as vertical gastrectomy and gastric bypass, not only helps patients lose weight significantly, but can also have positive effects on the management and, in some cases, remission of these comorbid diseases.
In this blog post, we will explore the impact of the bariatric surgery in the most common comorbid conditions associated with obesity. From type 2 diabetes to sleep apnea, we will examine how this surgical procedure can improve the health and well-being of patients, giving them a new opportunity for a healthier and more active life.
Relationship between obesity and comorbid diseases
Obesity is a significant risk factor for the development of several comorbid diseases that can affect a person's health and well-being. This relationship between obesity and additional medical conditions is complex and multifaceted, but has been consistently established in medical research.
One of the comorbid diseases most closely associated with obesity is type 2 diabetes. Obesity increases insulin resistance and the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes, which can lead to serious complications such as kidney disease, cardiovascular disease and neuropathy.
In addition, obesity is strongly related to high blood pressure, which is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases such as coronary heart disease, stroke and peripheral arterial disease. Excess weight puts additional pressure on the circulatory system, which can lead to increased blood pressure and an increased risk of cardiovascular complications.
Other comorbid conditions associated with obesity include respiratory disorders such as sleep apnea, which can lead to serious health problems if not properly treated. Obesity has also been linked to dyslipidemia, which is an imbalance in blood lipid levels and can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
In summary, obesity and comorbid diseases are closely interconnected, and addressing obesity can have a significant impact on the prevention and management of these additional medical conditions. The bariatric surgery has proven to be an effective tool in this regard, offering patients a way to address both obesity and its associated comorbid diseases.
control. This type of surgery not only helps patients lose weight effectively, but can also lead to dramatic improvements in insulin sensitivity and glycemic control.
Studies have shown that the majority of patients with type 2 diabetes who undergo bariatric surgery experience complete or partial remission of their disease. This means that many patients can reduce or even completely eliminate the need for anti-diabetic medications and, in some cases, even insulin.
The gastric sleeve and the gastric bypass are two of the most common bariatric procedures that have been associated with significant improvements in glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. These procedures not only reduce the stomach's ability to store food, but also alter the way the body absorbs and processes nutrients, which can have beneficial effects on blood sugar regulation.
In addition, bariatric surgery may also have long-term beneficial effects on the cardiovascular health of patients with type 2 diabetes. By improving glycemic control and promoting weight loss, these procedures can reduce the risk of serious cardiovascular complications, such as heart disease and stroke.
In summary, bariatric surgery can be an effective tool in the management and control of type 2 diabetes in patients with severe obesity. By helping patients lose weight and improve their insulin sensitivity, these procedures may offer new hope for those struggling with this chronic disease.
Effects on Hypertension and Cardiovascular Diseases
The relationship between the obesity and the arterial hypertension is well known, and the bariatric surgery has proven to be an effective tool in the management of this condition and its cardiovascular consequences. High blood pressure is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases such as coronary heart disease, stroke and peripheral arterial disease. Excess weight puts additional pressure on the circulatory system, which can lead to increased blood pressure and an increased risk of cardiovascular complications.
Studies have shown that bariatric surgery can have a positive impact on high blood pressure, leading to a significant reduction in blood pressure in many patients. Both the gastric sleeve as the gastric bypass have been shown to be effective in reducing blood pressure in obese patients with hypertension.
In addition to blood pressure reduction, bariatric surgery can also have beneficial effects on overall cardiovascular health. By promoting weight loss and improving control of risk factors such as high blood pressure and diabetes, these procedures can reduce the risk of serious cardiovascular disease, including heart disease and stroke.
In summary, bariatric surgery can have significant effects on high blood pressure and associated cardiovascular disease. By addressing obesity and its comorbidities, these procedures can improve patients' cardiovascular health and reduce their risk of serious long-term complications.
Improvements in Sleep Apnea and Other Respiratory Conditions
The sleep apnea is a respiratory condition commonly associated with obesity, which can have serious health consequences if not properly treated. Obesity can contribute to the development of sleep apnea by increasing the accumulation of fatty tissue around the upper airway, which can obstruct airflow during sleep.
The bariatric surgery has been shown to be effective in improving sleep apnea and other related respiratory conditions in obese patients. By significantly reducing body weight and improving overall health, these procedures can help relieve airway obstruction and improve sleep quality.
Studies have shown that both the gastric sleeve as the gastric bypass can lead to significant improvements in sleep apnea in obese patients. After surgery, many patients experience a reduction in the severity of sleep apnea symptoms, including the frequency of apnea episodes and excessive daytime sleepiness.
In addition to sleep apnea, bariatric surgery can also have beneficial effects on other respiratory conditions, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). By reducing body weight and improving overall respiratory health, these procedures can help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life in patients with these chronic respiratory conditions.
In summary, bariatric surgery can offer an effective solution for sleep apnea and other respiratory conditions in obese patients. By addressing obesity and its comorbidities, these procedures can improve patients' long-term respiratory health and quality of life.
To conclude
The bariatric surgery emerges as a comprehensive tool in the management of comorbid conditions associated with obesity. From type 2 diabetes to arterial hypertension and sleep apnea, this surgical intervention has proven to be effective in improving the health and quality of life of patients with severe obesity.
One of the greatest achievements of bariatric surgery is its impact on the remission of type 2 diabetes. Most patients experience a significant reduction in the need for anti-diabetic medications after the procedure, giving them new hope in the management of this chronic disease.
In addition, bariatric surgery offers significant benefits in the management of high blood pressure and associated cardiovascular disease. By lowering blood pressure and improving control of risk factors, such as obesity and diabetes, these procedures can reduce the risk of serious complications, such as heart disease and stroke.
Another highlight is the improvement in sleep apnea and other respiratory conditions. Bariatric surgery can relieve airway obstruction and improve sleep quality in obese patients, resulting in significant improvement in their respiratory health and overall quality of life.
In summary, bariatric surgery not only offers an effective solution to obesity, but can also have a transformative impact on associated comorbid conditions, giving patients a new opportunity for a healthier and more active life.