The fight against obesity is a challenging battle that affects millions of people worldwide. For those who have exhausted other weight-loss options without success, the bariatric surgery is presented as an effective and often transformative solution. Within the field of bariatric surgery, two main procedures have gained popularity: the gastric bypass and the gastric sleeve.
Both procedures offer hope for those looking to lose weight and improve their health, but it is crucial to understand the differences between them in order to make an informed decision about which might be the best option. In this blog post, we will explore gastric bypass and gastric sleeve in detail, breaking down their techniques, benefits and associated risks, to help you determine which is the best option for you.
As we explore the differences between these procedures, we will also consider factors such as expected weight loss, eligibility requirements and long-term considerations. If you are considering bariatric surgery as an option for managing your obesity, this guide will provide you with the information you need to take the next step with confidence.
Description and differences between each procedure
The gastric bypass and the gastric sleeve are two surgical procedures bariatric which share the common goal of helping patients lose weight and improve their health. However, they differ in their surgical approach and technique, which can influence patient outcomes and postoperative experience.
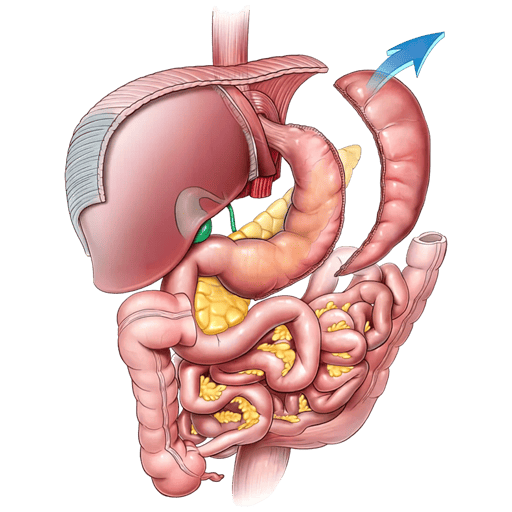
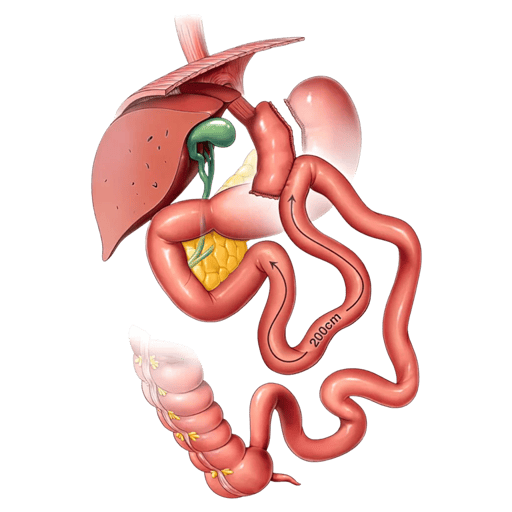
The gastric bypass involves the creation of a small pouch in the upper part of the stomach, which is disconnected from the rest of the stomach and attaches directly to the small intestine. This reduces the amount of food that can be consumed and the amount of calories and nutrients the body absorbs. In addition, gastric bypass may affect the way the body processes food and may induce a faster feeling of fullness.
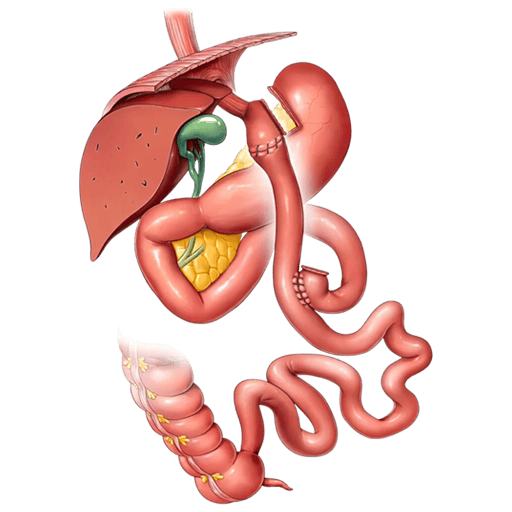
On the other hand, the gastric sleeve implica la remoción de una gran parte del estómago, dejando un estómago más pequeño en forma de tubo o «manga». A diferencia del bypass gástrico, no se realizan desviaciones en el intestino delgado, lo que significa que la absorción de nutrientes no se ve afectada de la misma manera. Sin embargo, la manga gástrica reduce significativamente la capacidad del estómago para contener alimentos, lo que resulta en una sensación de saciedad más temprana y una menor ingesta de alimentos.
In terms of weight loss, it has been observed that gastric bypass tends to produce more rapid weight loss in the first few months after surgery, whereas gastric sleeve may offer more gradual but sustained weight loss over time. In addition, gastric bypass has been associated with a greater resolution of metabolic diseases, such as type 2 diabetescompared to the gastric sleeve.
While both procedures can be effective in managing obesity, it is important to consider the differences between gastric bypass and gastric sleeve, as well as your own needs and health goals, when making a decision about which might be the best option for you.
Expected weight loss
The bariatric surgery is considered an effective approach to weight loss in severely obese patients. When it comes to determining the expected weight loss, both the gastric bypass as the gastric sleeve have shown encouraging results.
With the gastric bypassIn the first year after surgery, patients usually experience more rapid initial weight loss due to the combination of reduced stomach size and alteration of the digestive system. During the first year after surgery, patients can expect to lose between 60% and 80% of their excess weight.
On the other hand, the gastric sleeve tends to produce a more gradual but steady weight loss over time. By reducing the size of the stomach and limiting the amount of food that can be consumed, patients can expect to lose between 50% and 70% of their excess weight during the first two years after surgery.
It is important to keep in mind that the expected weight loss may vary depending on the patient and his or her compliance with postoperative recommendations, including changes in diet and physical activity. In addition, the quality of weight loss, including improvement in health conditions associated with obesity, should also be considered when evaluating the results of bariatric surgery.
Benefits and risks
The bariatric surgery offers a number of significant benefits for those struggling with obesity, but it also carries certain risks that should be carefully considered.
Benefits:
- Significant weight lossBoth the gastric bypass as the gastric sleeve have been shown to be effective in reducing excess weight, which can lead to significant improvements in health and quality of life.
- Resolution of comorbiditiesBariatric surgery can help control or even resolve obesity-related diseases, such as obesity. type 2 diabetesthe arterial hypertension and the sleep apnea.
- Improved quality of lifeMany patients experience an improvement in their general well-being and ability to participate in daily activities after surgery.
- Increased longevityStudies have shown that bariatric surgery can reduce the risk of premature mortality in patients with severe obesity.
Risks:
- Surgical complicationsAs with any surgical procedure, there are risks of complications during and after surgery, such as infection, bleeding and suture line leakage.
- Nutritional deficienciesBariatric surgery can interfere with the absorption of certain nutrients, which can lead to long-term nutritional deficiencies if not properly managed.
- Adverse reactionsSome patients may experience short- and long-term side effects, such as intolerance to certain foods, nausea and vomiting, and gastrointestinal problems.
- Follow-up requirementsPatients should engage in regular medical follow-up after surgery to monitor their progress and address any problems that may arise.
Despite these risks, many patients find that the benefits of bariatric surgery far outweigh the risks, especially when combined with a comprehensive approach to obesity management.
Long-term considerations of each procedure
After undergoing bariatric surgery, it is critical to consider the long-term implications of each procedure. Both the gastric bypass as the gastric sleeve can have lasting effects on the patient's health and lifestyle.
In the case of the gastric bypassIn addition, patients should be aware of the possibility of developing certain long-term complications, such as nutritional deficiencies due to altered nutrient absorption. It is essential that patients follow a lifelong vitamin and mineral supplementation plan to avoid deficiencies, especially of vitamins B12, D and iron. In addition, some patients may experience dumping syndrome, a series of unpleasant symptoms that occur when sugar-rich foods move rapidly from the stomach into the small intestine. Dumping syndrome can cause nausea, sweating, dizziness and diarrhea, and may require dietary changes to control symptoms.
On the other hand, the gastric sleeve also has long-term considerations that must be taken into account. Although gastric sleeve does not affect nutrient absorption as gastric bypass does, patients should be aware that the reduced stomach may cause permanent changes in eating habits and food tolerance. It is important to follow a balanced diet and avoid overeating to maintain long-term weight loss. In addition, some patients may experience gastric dilatation over time, which can result in weight gain if not properly addressed.
Both gastric bypass and gastric sleeve can provide satisfactory long-term results in terms of weight loss and improved health. However, it is important that patients understand the long-term implications of each procedure and are committed to following a plan of medical follow-up and lifestyle changes to ensure the long-term success of their bariatric surgery.