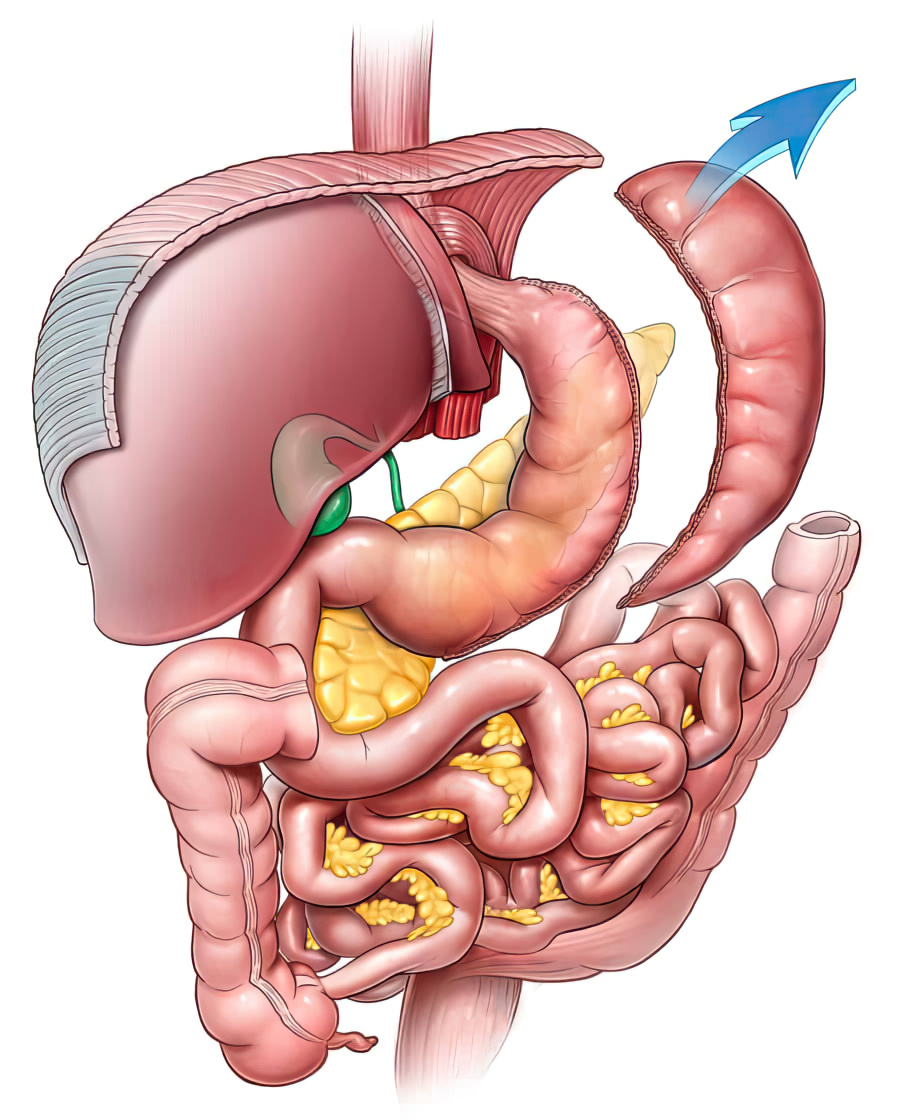
Abu Gazala, S., & Schlager, A. (2021). Single incision laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. In M. Gagner, M. Ramos-Levi, & A. Khorgami (Eds.), Sleeve gastrectomy: Surgical techniques, clinical aspects and complications (pp. 93-103). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-64484-0_7
American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) (2020). Bariatric surgery procedures. Retrieved from https://asmbs.org/patients/bariatric-surgery-procedures
Angrisani, L., Santonicola, A., Iovino, P., Vitiello, A., Higa, K., Himpens, J., ... Buchwald, H. (2020). Bariatric surgery and endoluminal procedures: IFSO Worldwide Survey 2018. Obesity Surgery, 30(12), 4816-4823. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-020-04978-1.
Phillips, M. S., Marks, J. M., Roberts, K., Tacchino, R., Onders, R., & DeNoto, G. (2018). Intermediate results of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and single-incision laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy in 376 patients. Surgical Endoscopy, 32(2), 904-910. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-017-5815-1.
Rosenthal, R. J., Diaz, A. A., Arvidsson, D., Baker, R. S., Basso, N., Bellanger, D., ... Weiner, R. (2013). International Sleeve Gastrectomy Expert Panel Consensus Statement: best practice guidelines based on experience of>12,000 cases. Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases, 8(1), 8-19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soard.2011.10.019.
Saber, A. A., El-Ghazaly, T. H., Dewoolkar, A. V., & Slayden, G. (2017). Early experience with single incision transumbilical laparoscopic adjustable laparoscopic gastric banding using the SILS Port. International Journal of Surgery, 39, 87-92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2017.01.110.
World Health Organization (WHO) (2021). Obesity and overweight. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight